by Timothy Don

In my capacity as art editor at Lapham’s Quarterly, I’ve spent the last six weeks researching images for our upcoming issue on TRADE. It was not a thematic that excited me when I started, I have to admit—I’m a curator and a writer, not a businessman or an economist, dammit! But after looking at more than 10,000 paintings, sculptures, and photographs that limn the human urge to exchange goods, a faint thrill and a growing sense of despair have both begun to take root.I’ve peered into the faces of Ferdinand Bol’s Syndics of the Wine Traders Guild of Amsterdam from 1660, looking for signs of avarice, prudence, and rectitude.

I’ve turned in my hands a 3rd century terracotta figurine of a camel carrying transport amphora (a secular, material expression of the nativity scene I just disassembled with my daughter). I’ve flipped through Alex Majoli’s 1999 series of photographs of the Roque Santeiro in Angola, the largest open-air market in Africa. According to Alex, the Roque attracts roughly one million people per day, and its vendors sell anything and everything: food, weapons, drugs, even people. It hosts church services and marriages. It shelters war cripples, homeless refugees, police, prostitutes, and the insane. Babies are born and the dead are interred within and beneath its stalls. At this “market of the damned,” Hieronymus Bosch’s 15th century visions of hell have been fully realized by the predations of 20th century capitalism.

A line and a theme have emerged through the iconography I’ve been following: to trade is human. We buy and we sell; we exchange, barter, haggle, negotiate, promise, vouchsafe, con, steal, acquire, and unload. It’s what we do; it’s what we’ve always done. The allure of trade lies not so much in the goods amassed as in the frisson of exchange: the contact with another human being that occurs in the act of trade. The slipping-ness from one to another. The handshake, the greased palm, the unctuous smile. The flow, the liquidity. The intimate bond that is established between two people when they make a deal. To trade is human. It’s dirty and oily and sexy.
And yet, underneath trade, there is something else going on. Something very faint, something very fragile, something that only adds to the excitement and the value of the goods on the table, is put at risk each time a trade is made. This something is trust. Read more »




 “I’m on a roadside perch,” writes Ghalib in a letter, “lounging on a takht, enjoying the sunshine, writing this letter. The weather is cold…,” he continues, as he does in most letters, with a ticklish observation or a humble admission ending on a philosophical note, a comment tinged with great sadness or a remark of wild irreverence fastened to a mystic moment. These are fragments recognized in Urdu as literary gems because they were penned by a genius, but to those of us hungry for the short-lived world that shaped classical Urdu, those distanced from that world in time and place, Ghalib’s letters chronicle what is arguably the height of Urdu’s efflorescence as well as its most critical transitions as an elite culture that found itself wedged between empires (the Mughal and the British), and eventually, many decades after Ghalib’s death, between two countries (Pakistan and India).
“I’m on a roadside perch,” writes Ghalib in a letter, “lounging on a takht, enjoying the sunshine, writing this letter. The weather is cold…,” he continues, as he does in most letters, with a ticklish observation or a humble admission ending on a philosophical note, a comment tinged with great sadness or a remark of wild irreverence fastened to a mystic moment. These are fragments recognized in Urdu as literary gems because they were penned by a genius, but to those of us hungry for the short-lived world that shaped classical Urdu, those distanced from that world in time and place, Ghalib’s letters chronicle what is arguably the height of Urdu’s efflorescence as well as its most critical transitions as an elite culture that found itself wedged between empires (the Mughal and the British), and eventually, many decades after Ghalib’s death, between two countries (Pakistan and India).

 Robert Morris died last month on November 28th at the ripe old age of 87. Very ripe indeed. If he was a fig he’d have been all jammy inside, dribbling the honeyed sugars of maturation. But he’s dead, and I’m glad he’s dead. Let me step back before explaining why – this isn’t an exposition, this is an obituary; I’m grieving; this is diffused ramblings at a podium. I went to Hunter College for undergraduate philosophy and flirted with the art department quite a bit. Morris’ legacy loomed large and hard over the department as he had both attended grad school and taught there. Any course in the art department was bound to encounter his work or his writings. I must have been assigned “Notes on Sculpture” a dozen times. Morris was, and still is, a great artist. His was a scholarly brand of art; neither annoying like Joseph Kosuth, nor dehydrated like Hans Haacke. No, Morris was a genuine student of art and thought. He studied its history, wrote about it emphatically, and contributed to its heritage. It is not difficult to view him as one of the several pillars that contemporary art stands upon today, and feel indebted to his legacy. One of his first well regarded artworks was Box for Standing, which was a handmade wooden box roughly the size of a coffin that fit Morris neatly. How fitting then, that his exit from this life should perhaps be in a box bespoke for his corpse, roughly the same size as his original Box? His expiration has a funny effect on that work, Box for Standing, where his actual death gives the work one last veneer of meaning to stack upon all the other layers. One might have seen similarity between the Box for Standing and funerary vessels before Morris died, but afterward it would be reckless not to see it. The work goes from being a sparse theatrical gesture contained in minimal sculpture, to something like a pragmatic Quaker coffin, verging on bleak humor.
Robert Morris died last month on November 28th at the ripe old age of 87. Very ripe indeed. If he was a fig he’d have been all jammy inside, dribbling the honeyed sugars of maturation. But he’s dead, and I’m glad he’s dead. Let me step back before explaining why – this isn’t an exposition, this is an obituary; I’m grieving; this is diffused ramblings at a podium. I went to Hunter College for undergraduate philosophy and flirted with the art department quite a bit. Morris’ legacy loomed large and hard over the department as he had both attended grad school and taught there. Any course in the art department was bound to encounter his work or his writings. I must have been assigned “Notes on Sculpture” a dozen times. Morris was, and still is, a great artist. His was a scholarly brand of art; neither annoying like Joseph Kosuth, nor dehydrated like Hans Haacke. No, Morris was a genuine student of art and thought. He studied its history, wrote about it emphatically, and contributed to its heritage. It is not difficult to view him as one of the several pillars that contemporary art stands upon today, and feel indebted to his legacy. One of his first well regarded artworks was Box for Standing, which was a handmade wooden box roughly the size of a coffin that fit Morris neatly. How fitting then, that his exit from this life should perhaps be in a box bespoke for his corpse, roughly the same size as his original Box? His expiration has a funny effect on that work, Box for Standing, where his actual death gives the work one last veneer of meaning to stack upon all the other layers. One might have seen similarity between the Box for Standing and funerary vessels before Morris died, but afterward it would be reckless not to see it. The work goes from being a sparse theatrical gesture contained in minimal sculpture, to something like a pragmatic Quaker coffin, verging on bleak humor.  In reviewing “Intimations of Ghalib”, a new translation of selected ghazals of the Urdu poet Ghalib by M. Shahid Alam, let it be said at the outset that translating classical Urdu ghazal into any language – possibly excepting Persian – is an almost impossible task, and translating Ghalib’s ghazals even more so. The use of symbolism, the aphoristic aspect of each couplet, the frequent play on words, and the packing of multiple meanings into a single verse are all too easy to lose in translation. And no Urdu poet used all these devices more pervasively and subtly than Ghalib, and even learned scholars can disagree strongly on the “correct” meaning of particular verses. As such, Alam set himself an impossible task, and the result is, among other things, a demonstration of this.
In reviewing “Intimations of Ghalib”, a new translation of selected ghazals of the Urdu poet Ghalib by M. Shahid Alam, let it be said at the outset that translating classical Urdu ghazal into any language – possibly excepting Persian – is an almost impossible task, and translating Ghalib’s ghazals even more so. The use of symbolism, the aphoristic aspect of each couplet, the frequent play on words, and the packing of multiple meanings into a single verse are all too easy to lose in translation. And no Urdu poet used all these devices more pervasively and subtly than Ghalib, and even learned scholars can disagree strongly on the “correct” meaning of particular verses. As such, Alam set himself an impossible task, and the result is, among other things, a demonstration of this.
 In 2018, Earth picked up about 40,000 metric tons of interplanetary material, mostly dust, much of it from comets. Earth lost around 96,250 metric tons of hydrogen and helium, the lightest elements, which escaped to outer space. Roughly 505,000 cubic kilometers of water fell on Earth’s surface as rain, snow, or other types of precipitation. Bristlecone pines, which can live for millennia, each gained perhaps a hundredth of an inch in diameter. Countless mayflies came and went. As of this writing, more than one hundred thirty-six million people were born in 2018, and more than fifty-seven million died.
In 2018, Earth picked up about 40,000 metric tons of interplanetary material, mostly dust, much of it from comets. Earth lost around 96,250 metric tons of hydrogen and helium, the lightest elements, which escaped to outer space. Roughly 505,000 cubic kilometers of water fell on Earth’s surface as rain, snow, or other types of precipitation. Bristlecone pines, which can live for millennia, each gained perhaps a hundredth of an inch in diameter. Countless mayflies came and went. As of this writing, more than one hundred thirty-six million people were born in 2018, and more than fifty-seven million died.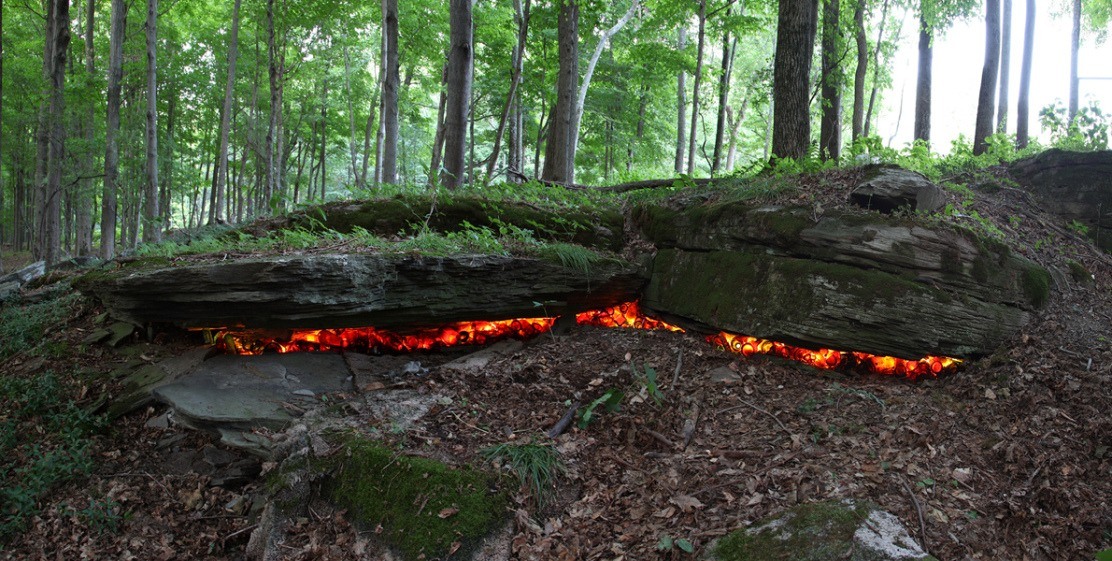
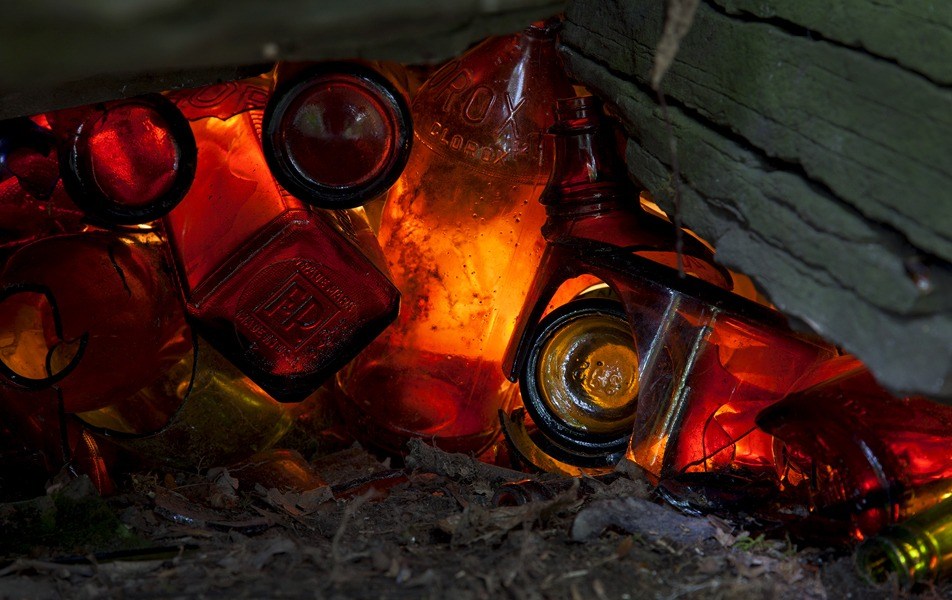


 It is simultaneously awkward and exciting to read about your own consciously and responsibly adopted beliefs as something to be anatomized. It is also something atheists are not always much disposed to. On the contrary, perhaps: many forms of atheism present themselves as a consequence of free thought, of emancipation from tradition. The internal logic of their arguments prescribes that while religious beliefs, being non-rational, are in need of cultural or psychological explanation, atheism is really just what you will gravitate towards once you finally start thinking. One question here will be whether this is necessarily the case.
It is simultaneously awkward and exciting to read about your own consciously and responsibly adopted beliefs as something to be anatomized. It is also something atheists are not always much disposed to. On the contrary, perhaps: many forms of atheism present themselves as a consequence of free thought, of emancipation from tradition. The internal logic of their arguments prescribes that while religious beliefs, being non-rational, are in need of cultural or psychological explanation, atheism is really just what you will gravitate towards once you finally start thinking. One question here will be whether this is necessarily the case. Certain phrases choke us with their ubiquity at some point:
Certain phrases choke us with their ubiquity at some point: