Francis Collins in NIH Director’s Blog:
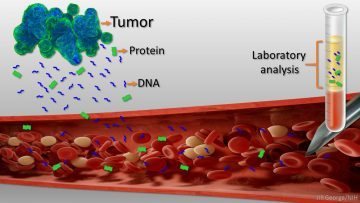 Early detection usually offers the best chance to beat cancer. Unfortunately, many tumors aren’t caught until they’ve grown relatively large and spread to other parts of the body. That’s why researchers have worked so tirelessly to develop new and more effective ways of screening for cancer as early as possible. One innovative approach, called “liquid biopsy,” screens for specific molecules that tumors release into the bloodstream.
Early detection usually offers the best chance to beat cancer. Unfortunately, many tumors aren’t caught until they’ve grown relatively large and spread to other parts of the body. That’s why researchers have worked so tirelessly to develop new and more effective ways of screening for cancer as early as possible. One innovative approach, called “liquid biopsy,” screens for specific molecules that tumors release into the bloodstream.
Recently, an NIH-funded research team reported some encouraging results using a “universal” liquid biopsy called CancerSEEK [1]. By analyzing samples of a person’s blood for eight proteins and segments of 16 genes, CancerSEEK was able to detect most cases of eight different kinds of cancer, including some highly lethal forms—such as pancreatic, ovarian, and liver—that currently lack screening tests. In a study of 1,005 people known to have one of eight early-stage tumor types, CancerSEEK detected the cancer in blood about 70 percent of the time, which is among the best performances to date for a blood test. Importantly, when CancerSEEK was performed on 812 healthy people without cancer, the test rarely delivered a false-positive result. The test can also be run relatively cheaply, at an estimated cost of less than $500.
Cancers arise when gene mutations occur in individual cells, dysregulating their normal growth and allowing them to divide without the usual restraints. As the clump of cancer cells expands, some die and bits of their mutated DNA can end up in the bloodstream. Liquid biopsies then search the blood for those bits of DNA carrying mutations associated with cancer. In 2016, the FDA approved the first liquid biopsy test for detecting a single mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer for use in guiding treatment decisions of people already known to have this type of cancer [2]. But developing a liquid biopsy test that could screen apparently healthy people for a variety of early cancers has proven a much greater challenge.
More here.
